In my previous blog I have shown how you can generate other number systems (binary, Hexa, and octal) from decimal using a built-in library.
In this blog, I will be showing the same output generation but with a different procedure. We will not use a built-in function. Instead, we will build our own function to complete the task.
Decimal to Binary:
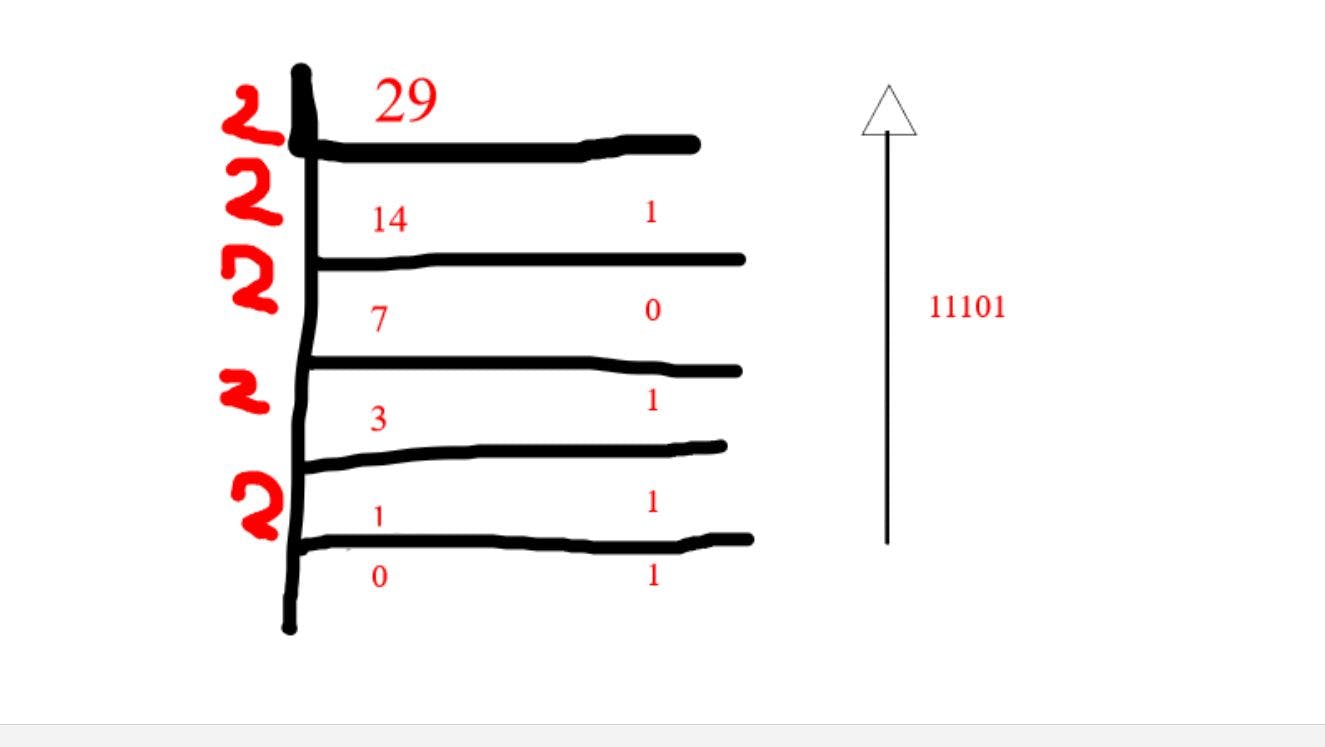
This is the conventional way we convert decimal to binary. If you don't know how this works check here
def BinaryConvert(n):
global binary
if n>= 1:
binary+=str(n%2)
BinaryConvert(n // 2)
return binary[::-1]
print("Enter decimal:")
n = int(input())
print("Binary :")
print((BinaryConvert(n)))
Enter decimal:
29
Binary :
11101
Decimal to Hexadecimal:
hexa=''
def HexaConvert(n):
global hexa
if n>= 1:
hexa+=str(n%16)
HexaConvert(n // 16)
return hexa[::-1]
print("Enter decimal:")
n = int(input())
print("\nHexadecimal :")
print((HexaConvert(n)))
Output:
Enter decimal:
29
Hexadecimal :
131
Decimal to Octal:
octa=''
def OctaConvert(n):
global octa
if n>=1:
octa+=str(n%8)
OctaConvert(n//8)
return octa[::-1]
print("Enter decimal:")
n = int(input())
print("\nOctal :")
print((OctaConvert(n)))
Output:
Enter decimal:
29
Octal :
35
The trick here is to divide the decimal input with the base in which number system you want to convert and then store the variable in a string sequentially and then reverse the string to get the result. Every function here is returning the reversed string using the slicing method in python. And the reason we are getting the result by reversing the string is after dividing the last remainder of the decimals are counted as MSB(most significant bit)